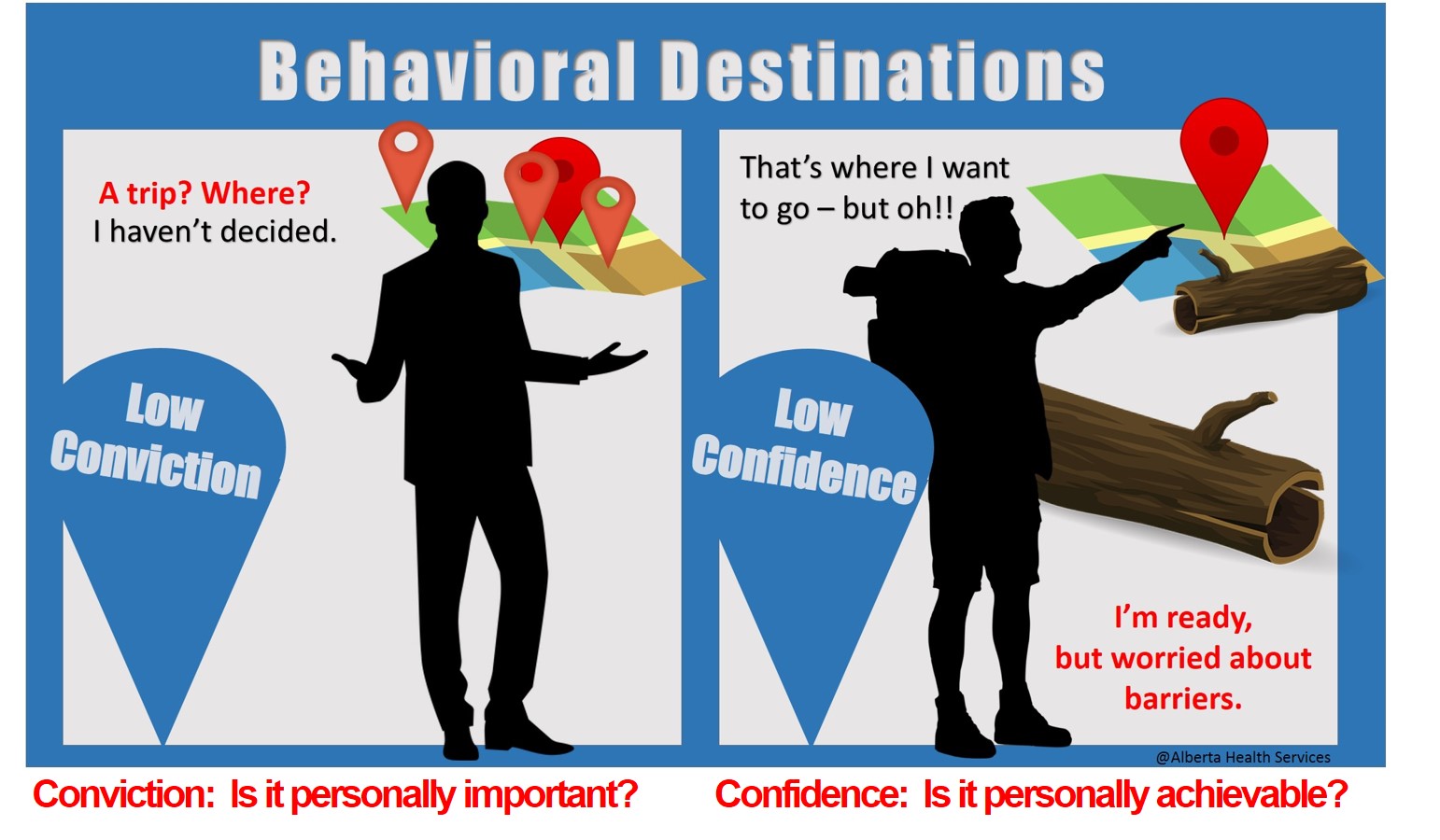
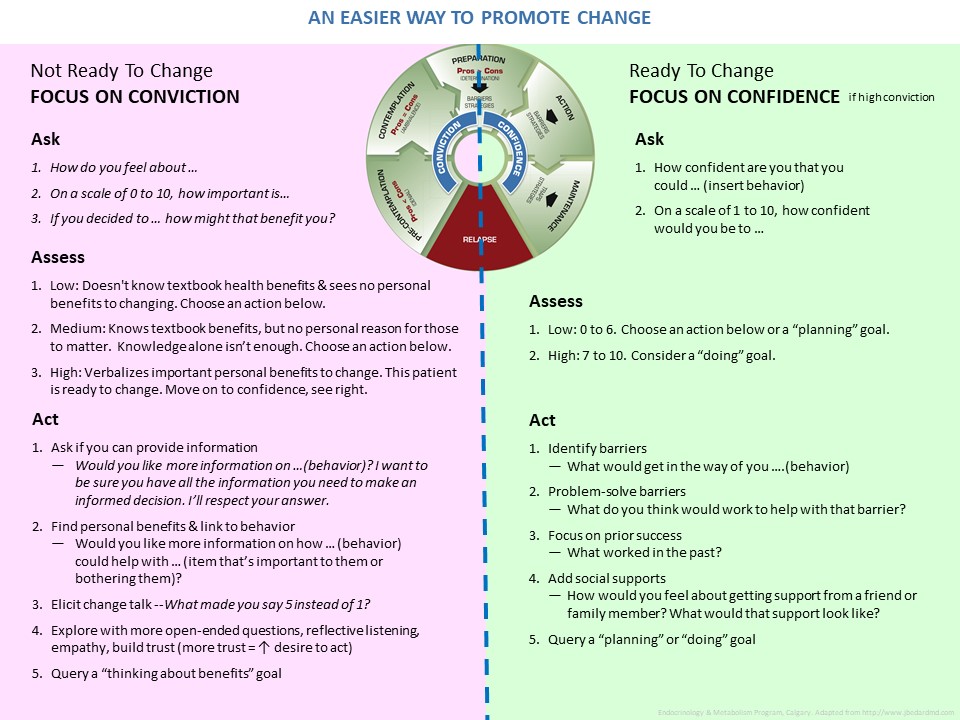
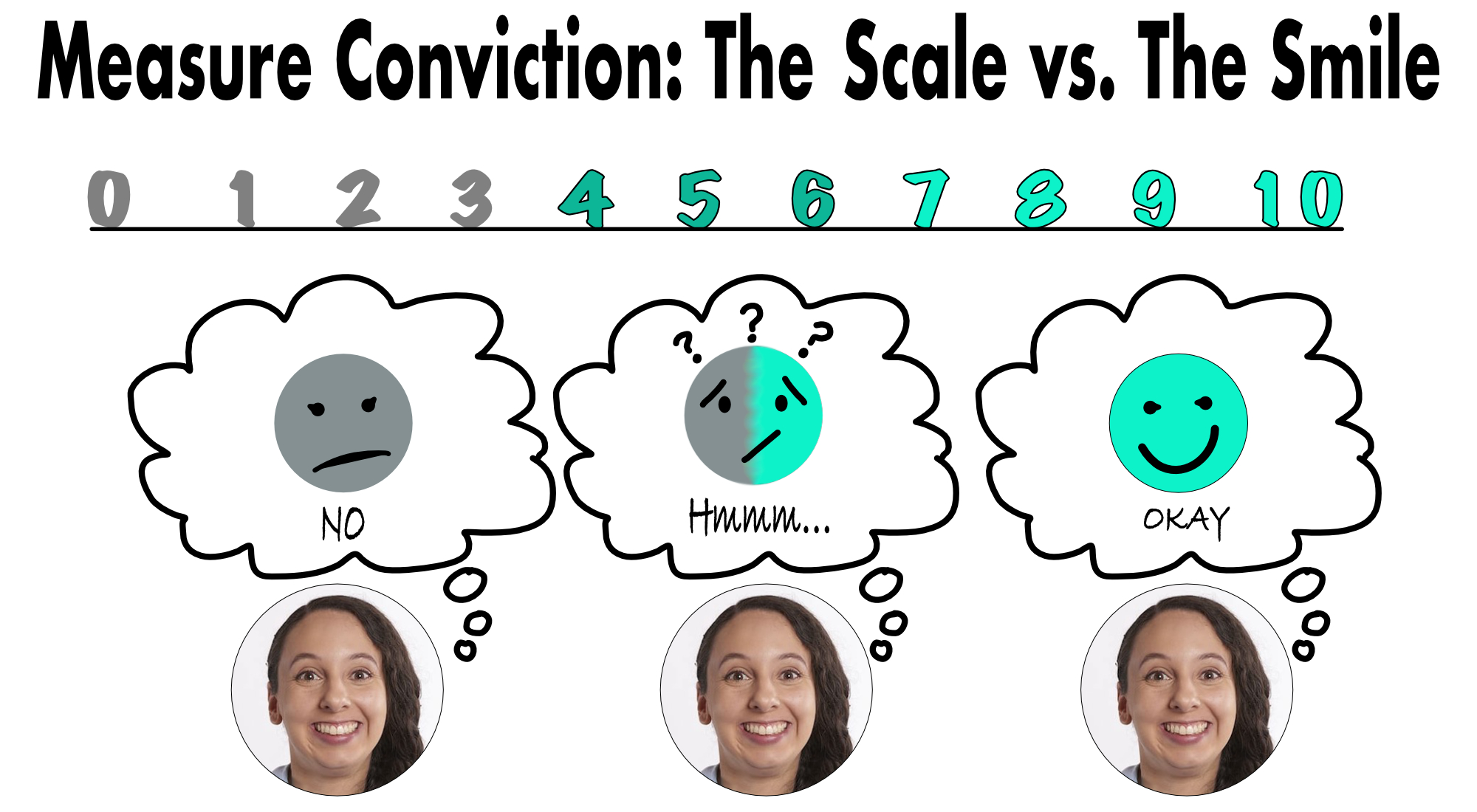
One of the most challenging roles of a diabetes educator is to help those who seem stuck - those unable to make a specific behaviour change, appointment after appointment. Perhaps change isn't desired or, perhaps it is. We know that is hard; so is your job. Hopefully this page provides some useful reminders to help.
We hope this page will help you:
- Remember the value of assessing patient conviction & confidence when discussing change.
- Assess conviction and confidence in a few cases.
- Choose next steps to help patients move towards behaviour, using a one-page summary tool.
Some answers are found by reading the information in this section. Other answers are found by asking yourself what, if anything, you want more of in your practice.
1. When referring to “conviction” in terms of health behavior change, which definition(s) are accurate.
- A belief that something is personally achievable.
- A belief that something is personally important and provides personal benefits.
- A declaration that someone is guilty of a criminal offence.
- All of the above
- None of the above.
2. These are some potential benefits for patients when we focus on conviction & confidence in our appointments. Think of your last month of work. Which of these (if any) would you most like to see improved or added for your patients? Choose as many as apply.
- Them leaving your office feeling they were heard and respected
- Them weighing pros & cons so they know it's their informed decision about their health, not you making their decisions
- Them making more meaningful changes, meaningful to them personally
- Them making faster behaviour changes, instead of "stuck" not moving
- None at this moment
3. These are some potential benefits for us, as healthcare providers, when we focus on conviction & confidence in our appointments. Think of your last month of work. Which of these would you most like to see improved or added for yourself. Choose as many as you like.
- Understanding my patients' internal, personal needs, concerns & perspective better
- Improving rapport & communications with patients
- Saving appointment time
- Decreasing frustrations
- Increasing work satisfaction
- None at this moment
4. Conviction & Confidence can be summarized as "Belief in importance" and "Belief in ability". When considering behaviour change, which of these are true? Click all that apply.
- Assessing for confidence (belief in ability to do behaviour) should usually come first
- Assessing for conviction (belief in importance to do behaviour) should usually come first
- It doesn't matter the order
- Asking questions like, "What's getting in the way of you doing X?" or "What worked last time you did X?" are actions to help address confidence. Many health care providers are excited to help patients and start here first.

The answers to these questions are found by reading the information in the Conviction Tabs. You might answer these questions to start and come back afterwards to answer them again, after you've read the information on conviction.
- Which of these is the LEAST desirable question to ask to assess conviction? (Note X = the behavior change). Pick only one answer.
- On a scale of 1 to 10 how important is X to you?
- How do you feel about X?
- Would you be agreeable to X?
- How do you think X will benefit you?
- These are all great ways to assess conviction.
- None of these are used to assess for conviction.
- A diabetes educator has been seeing their patient, Alex, for years and always looks forward to their friendly appointments. They have great rapport. This visit, the educator explains the benefit of doing behavior “X” then asks if Alex could do that. Alex smiles, nods yes and moves into their trademark jokes. The appointment ends on time and in good spirits.
Choose the one best statement.- Alex could have low conviction (they don't think the behavior is important)
- Alex could have high conviction (they think the behaviour is very important)
- Alex could feel alienated.
- Any of the above
- I’m not sure
- In general, which strategies below could an educator use to help a person increase their conviction to do something?
- Educate, with permission
- Help the patient identify personal benefits
- Build rapport. Respect they may have other priorities (perhaps even assess for diabetes distress)
- All of the above
- None of these address building conviction.
-
Don't answer this question the first time around. Consider answering it the second time through. What, if anything, has this review of conviction done for you?
- It reinforced that you've got great skills and you'll work to keep them.
- It made you want to use your current skills more often.
- You learned at least one new tidbit and want to try it.
- You have low conviction for using these skills, but you have great personal reasons for that and you know that we respect you. :-)

The answers to these questions are found by reading the information in the Confidence Tabs.
- Choose the one incorrect statement.
- If confidence is assessed as high, there is little need to assess for conviction as it will likely be high. .
- How confident do you feel about ____ (insert behaviour)?" is a good assessment question.
- "On a scale of 1 – 10, how CONFIDENT are you that you could _____(insert behaviour)?" is a good assessment question
- Many healhcare providers jump to confidence building first, and may miss assessing conviction and assessing confidence.
- None of the above are incorrect.
- For someone with low to moderate confidence in a behavior change, a goal “to plan or to prepare” is a good start
- True
- False
- I don’t know
- All of these actions could help build confidence in patients. Choose the one that is least useful (and also happens to be least respectful).
- Offering up “what about this” suggestions
- Guiding the patient to make SMART goals
- Letting the patient decide if the goal type: “thinking about”, "planning or preparing" or "doing" goal.
- Asking what worked in the past to help them succeed with a difficult change
- Asking about social supports

The answers to these questions are found by reading the information in theTabs under "Keep in Mind".
- Something as simple as assessing/building conviction & confidence in the wrong order could result in:
- Disrespecting patients' autonomy and time
- Losing patients' trust
- Alienating patients, less honest answers
- Decreasing our ability as healthcare providers to help patients
- All of the above
- If we find ourselves repeating the same things, visit after visit, about a behaviour it might be best to reassess the patient's conviction (including diabetes distress).
- True
- False
- I'm not sure
- If the patient keeps repeating things in a visit, they likely don't feel heard on that point. Consider active listening and rephrasing back. True or false?
- True
- False
- I'm not sure

Case 1: Marta
The diabetes educator asks, “Marta, how do you feel doing some gluocose checks?”
Marta shrugs, then she sighs heavily with annoyance and says, “I used to do that. It will get in the way of my work. I have to take care of kids for a living. I run a daycare. It’s chaotic. Those kids keep me so busy! And, those kids are much more important than me!”

- Is now the right time to suggest making a SMART goal to start glucose testing?
- Is her conviction level (belief of personal importance) for testing glucose high?
- What other questions could you ask to clarify how important glucose testing is to her?
- On the one-page Big Summary: An Easier Way to Promote Change, will you choose actions (“ACT”) from the left side or the right side of the handout?